
- COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS SERIAL
- COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS ANDROID
- COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS TRIAL
- COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS FREE

COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS ANDROID
The right steps in cleaning one’s hand are as follows: Study module 1 - compare and contrast medical and surgical asepsis flashcards from Navneet Gill's class online, or in Brainscape's iPhone or Android app. In hand washing, one usually uses a soap, warm water, paper towel, trash basket, and wood sticks for nail cleaning.
COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS FREE
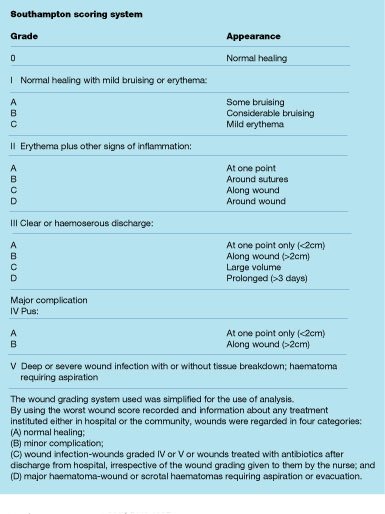
In a surgical application, sterile indicates totally free from all microbial forms either that can cause illness, decomposition, or fermentation. In surgery, there are trays & tables of instruments, sterile drapings of the patient, deep wounds or incisions, exposed bonesyou get the idea. Medical applications Aseptic Technique: Aseptic technique is commonly used in an operative field in medicine or surgery to prevent infection. Alternatively, an objective scoring system, like the ASEPSIS score, may yield more reliable measures for comparison.Hand washing is the act of cleaning one’s hand with or without the use of water or any liquid to prevent the spread of infection or virus and to increase psychological comfort. Answer: They are both used to prevent infection, but surgery is on a much larger scale & technique must be strictly adhered to. These findings could explain the wide variability in the literature and raise concern for the comparison of institutional surgical site infection rates as a quality indicator. Table 18-1 Comparing Medical and Surgical Asepsis Medical Asepsis Surgical Asepsis Definition Destroys microorganisms after they leave the body Purpose. This study demonstrates the relatively poor reliability of CDC definitions for surgical site infections in comparison with an objective scoring system. Alternatively, the ASEPSIS assessments demonstrated excellent interrater agreement between surgeons with 96% agreement (2.4%, 2.4%, and 3.6%) and a κ of 0.83. Data from the surgeons demonstrated significantly higher yet discrepant rates of infection by the CDC criteria, at 6.2%, 7.4%, and 14.1% with a κ of 0.55 indicating modest interrater agreement.

Four surgical site infections (2.4%) were identified by the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program.

One hundred seventy-one patients were included. These data were also compared with the institutional National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database. The interrater reliability of ASEPSIS and the CDC criteria were compared by using the κ statistic. Surgeons assigned an ASEPSIS score and identified surgical site infection by using CDC definitions. Patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery were selected. This study was conducted at an academic institution. Three attending surgeons independently reviewed blinded photographic/clinical data.
COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS SERIAL
This 24-month prospective study used serial photography of the wound. The aim of this study is to compare the interrater reliability of the ASEPSIS score vs CDC definitions in identifying surgical site infection. Weve got the study and writing resources you need.
COMPARE MEDICAL AND SURGICAL ASEPSIS TRIAL
Start your trial now First week only 4.99 arrowforward. It includes procedures used to decrease and prevent direct contact with blood or bodily fluids and emphasizes keeping the environment clean on a regular basis (Curchoe, Astle, & Hobbs, 2014). Solution for Implement recommended techniques for medicaland surgical asepsis. Alternatively, the ASEPSIS score is an objective scoring system based on the presence of clinical findings. Medical asepsis plays an integral role in infection control within a health care facility. CDC criteria include "diagnosis by attending physician," which can be subjective. Surgical site infection is common following colorectal surgery, yet the incidence varies widely.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
